Peripheral Arterial Disease – PAD
Watch the video above to learn about Peripheral Arterial Disease – PAD, and how I approach treating this with my patients. There's also more information below. As always, when you're ready, fill out the form on this page to request a consultation.
I walked in, they were so friendly and took amazing care of me. — Danielle
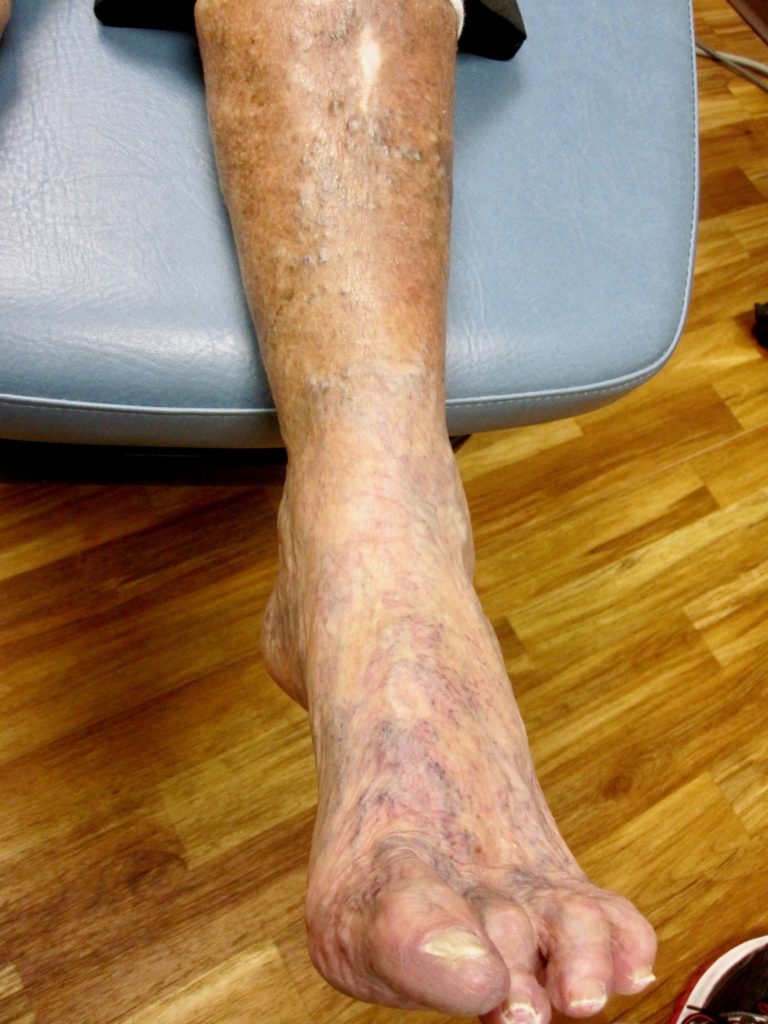
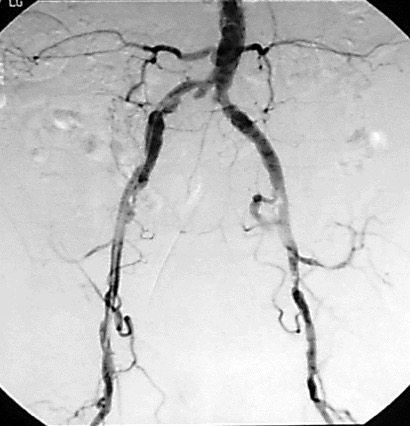
Peripheral arterial disease (PAD) occurs when there is decreased arterial blood flow to the lower extremities. With decreased arterial blood flow, tissues are deprived of oxygen and this can lead to such complications as pain, tissue death, infection, and lower extremity amputation. The diabetic foot is at higher risk for peripheral arterial disease.
Podiatrists like Dr. Stewart are frequently the first doctors to identify peripheral arterial disease in patients. Peripheral arterial disease is frequently found in conjunction with coronary artery disease (heart disease) and cerebrovascular disease (stroke) and therefore identifying and treating this condition is very important.
Symptoms
- Cramping in the back of the legs with ambulation known as intermittent claudication
- Non-healing or delayed healing wounds
- In more advanced stages, pain with rest. This pain is typically relieved when the leg is held down in the dependent position
- In severe disease there is tissue death also known as gangrene
Diagnosis
Patients suspected of having peripheral arterial disease are referred to a vascular specialist for management and treatment of the condition. Here they will undergo non-invasive arterial studies to determine the level and extent of the disease.
Treatment
The degree of peripheral arterial disease determines the treatment. Both conservative treatment and surgical treatment options are available and the vascular specialist determines the treatment.
I have severe nerve damage in both my feet from Type II Diabetes. I also suffer with other foot and ankle problems from the disease and at one point almost lost part of my left foot. Thankfully, Dr. Stewart was able to save my foot and prevent me from losing my leg. -Bonita Mays
Conservative treatment for Peripheral Arterial Disease – PAD includes:
- A walking program to improve collateral circulation
- Weight loss
- Smoking cessation
- Medications including cholesterol lowering drugs and anti-platelet drugs
- Management of risk factors including high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes
- Routine foot care and examination by a podiatrist like Dr. Stewart
When conservative treatment fails or more advanced treatments are required then surgical intervention is pursued. The goal of surgery is to improve arterial blood flow, heal any wounds that may be present, and prevent lower extremity amputation. The vascular specialist determines the surgical treatment.
Surgical treatment for Peripheral Arterial Disease – PAD includes:
- Endovascular procedures including balloon angioplasty, stenting, and removal of arterial plaque
- Open lower extremity bypass surgery
- In severe cases, the blood flow cannot be restored and either a podiatrist or vascular surgeon performs amputation. Amputation level is determined by the extent of the disease and can include toe amputation, partial foot amputation, below the knee amputation, and above the knee amputation
